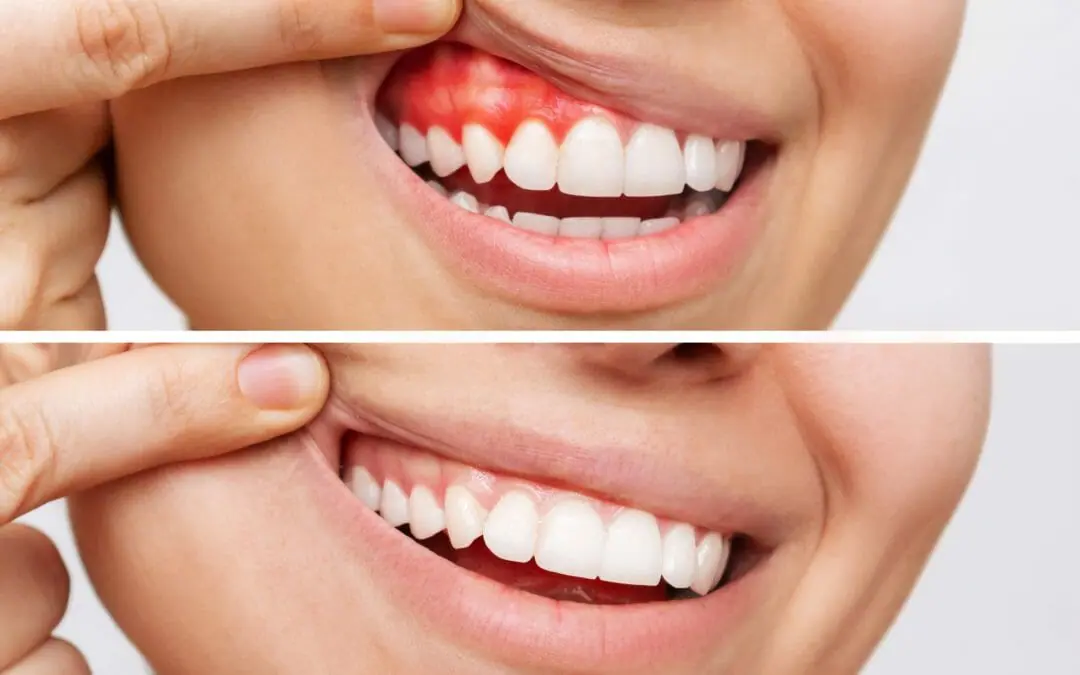
Periodontics is a specialized area of dentistry focusing on the structures that support your teeth, including the gums and bone. This field addresses the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases affecting these supporting tissues, and periodontists manage conditions from mild gum inflammation to advanced gum disease. Here are some periodontic treatments for gum disease and maintenance:
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is a common procedure for managing gum disease. It is a deep-cleaning method that goes below the gumline. A dental professional uses special instruments to remove plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces and from pockets that have formed between the gums and teeth. Root planing involves smoothing the tooth roots, which helps the gums reattach to the teeth. This non-surgical procedure is often the first step in treating gum disease because it helps reduce inflammation and allows the gums to begin healing. The process may be completed over one or more visits, depending on the extent of the condition.
Pocket Reduction
When gum disease progresses, the space between the gums and teeth, known as a periodontal pocket, may deepen. These deep pockets collect more plaque and bacteria, making them difficult to clean with regular brushing and flossing. Pocket reduction is a procedure designed to address this issue.
During this procedure, a periodontist folds back the gum tissue to remove the disease-causing bacteria. They then secure the tissue back in place. Irregular surfaces of the damaged bone may be smoothed to limit areas where bacteria hide. This procedure reduces the depth of the pockets and makes it easier for you and your dental team to keep the area clean.
Restoration Procedures
Gum disease may damage the bone and tissues that support your teeth, and periodontists are trained to repair this damage. Restoration techniques aim to regenerate lost bone and tissue, providing a healthier foundation for your teeth. Some options include:
- Bone grafting: Natural or synthetic bone is placed in a bone defect to encourage new bone growth.
- Soft-tissue grafting: This can help restore receded gum tissue.
- Guided tissue regeneration: This involves placing a small piece of mesh-like material between the bone and gum tissue, allowing the bone and connective tissue to regrow.
Crown Lengthening
In periodontics, crown lengthening is a procedure that adjusts the levels of gum and bone tissue around a tooth. Though sometimes performed for cosmetic reasons, it can also serve a functional purpose in restorative dentistry. The procedure exposes more of the tooth’s surface, which provides a stable base for placing a new crown or other restoration. A periodontist removes a small amount of gum tissue, and sometimes bone, to create a new gum-tooth relationship. This allows for a proper fit of the final restoration, which helps with its long-term stability and maintenance.
Learn More About Periodontics
Understanding the treatments available for gum disease can help you manage your oral health. Periodontics offers specialised solutions designed to address the structures that support your teeth, and maintaining healthy gums is a collaborative effort between you and your dentist. Schedule a consultation to discuss your symptoms and learn more about your treatment options.

Leave a Reply