A nuclear stress test is a diagnostic imaging assessment that evaluates blood flow to the heart at rest and during physical exertion. Physicians use this method to detect heart conditions that standard screenings may miss, offering a deeper look into cardiac function. Understanding the procedure helps you know what to expect. Here is more information on this test and what it involves:
What Is a Nuclear Stress Test?
A nuclear stress test combines a standard treadmill stress test with nuclear imaging to assess heart function comprehensively. The radioactive dye highlights blood flow, so the camera can detect areas with poor circulation or damage. This offers a more detailed view than a regular exercise stress test alone, which only records electrical activity.
It helps visualize the heart muscle’s ability to pump blood effectively under stress. The images reveal if the heart receives adequate blood flow when it beats faster, or if the flow is restricted. This information allows cardiologists to diagnose coronary artery disease accurately.
Why Is It Conducted?
Doctors recommend this test if a standard stress test does not provide sufficient information regarding your heart health. It is also suitable for patients who cannot exercise vigorously, as medication can simulate the effects of exercise on the heart. Your physician may order this exam if you experience unexplained chest pain or shortness of breath.
The test evaluates the effectiveness of previous heart treatments, such as stents or bypass surgery. It helps determine whether your heart is healthy enough for non-cardiac surgeries, and it assists in determining safe exercise levels. This diagnostic step aids in establishing the most appropriate course of action for managing heart conditions.
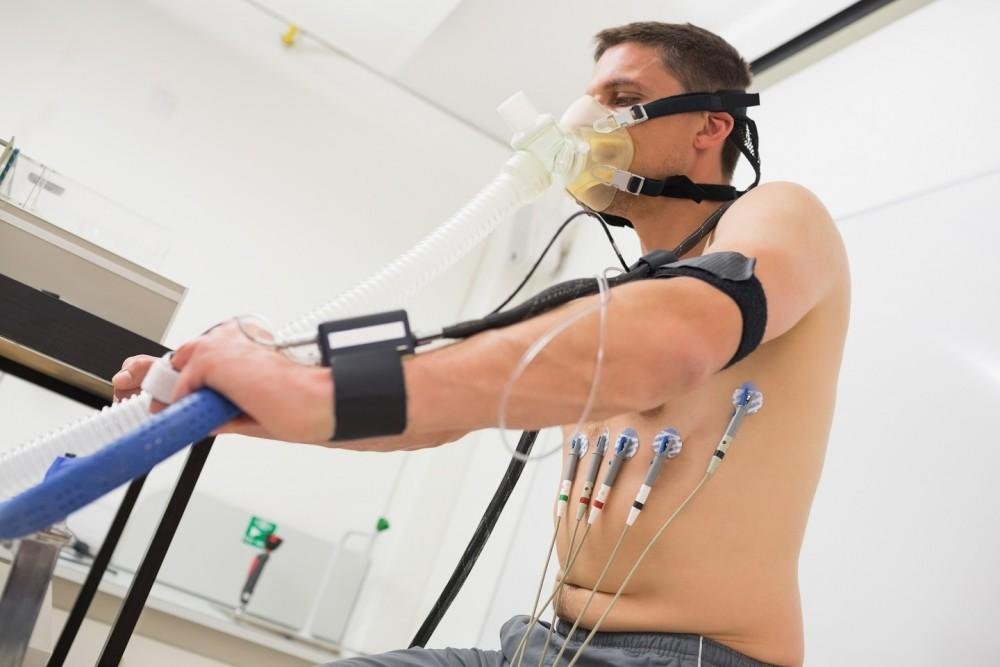
What Does the Procedure Involve?
Preparation begins before you arrive at the clinic, as you must fast for several hours. You should wear comfortable clothing and walking shoes, and you must avoid caffeine for 24 hours prior to the test. The medical staff will review your medications to decide if you need to pause any of them.
During the procedure, a radioactive tracer is injected into your arm, electrodes are placed on your chest, and you will walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike to gradually increase your heart rate. If you cannot exercise, the doctor administers medication to mimic the stress of physical activity. You receive another injection of the tracer when your heart rate reaches a target level.
What Are the Benefits?
The primary benefit is the high level of detail regarding blood flow to the heart muscle. The images allow doctors to pinpoint the exact location of blocked arteries, and they rule out significant blockages. It serves as a reliable method for assessing the risk of future heart attacks. Knowing the specific condition of your heart arteries helps you and your doctor to make informed health decisions.
What Results Can You Expect?
The results generally fall into the categories of normal, abnormal, or inconclusive. A normal result means blood flows freely through the coronary arteries during both rest and exercise, and this suggests that you do not have significant coronary artery disease or risk of a heart attack. An abnormal result indicates that blood flow is restricted to part of the heart. The doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, medication, or further testing depending on the severity of the findings.
Consult a Cardiologist Today
Understanding your heart health status helps prevent serious complications later. A cardiologist will review your symptoms and medical history, and they will decide if this test is right for you. Schedule an appointment to discuss your options and protect your heart.

Leave a Reply