Pulmonary function refers to how well the lungs work, specifically their ability to move air in and out and how they transfer gases into the bloodstream. Evaluating this function is a key component of respiratory health management. For children with respiratory conditions like asthma, pulmonary function tests (PFTs) provide information about their lung health. Here is more information on pulmonary function testing for asthmatic children:
What Is Pulmonary Function Testing?
Pulmonary function tests are a group of noninvasive procedures designed to assess lung function. These tests involve breathing into a machine that measures various aspects of lung performance. The results are then compared to predicted values. These values are calculated based on a child’s age, height, sex, and established reference standards for their demographic group. This comparison helps healthcare providers understand a child’s lung function.
Asthma Management
For children with asthma, PFTs serve multiple purposes throughout their care. They can help in the initial evaluation of symptoms, monitor the condition over time, and assess the effectiveness of treatments. While some assessments may begin at younger ages, more detailed tests are often used for children aged six and older.
Asthma Test Measurements
PFTs measure several key indicators of lung health. These include lung volume, which is the amount of air the lungs can hold, and flow rate, which is how quickly air can be moved in and out. Specific measurements like forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), and the FEV1/FVC ratio are commonly reviewed. These numbers provide detailed insights into how well the airways are functioning.
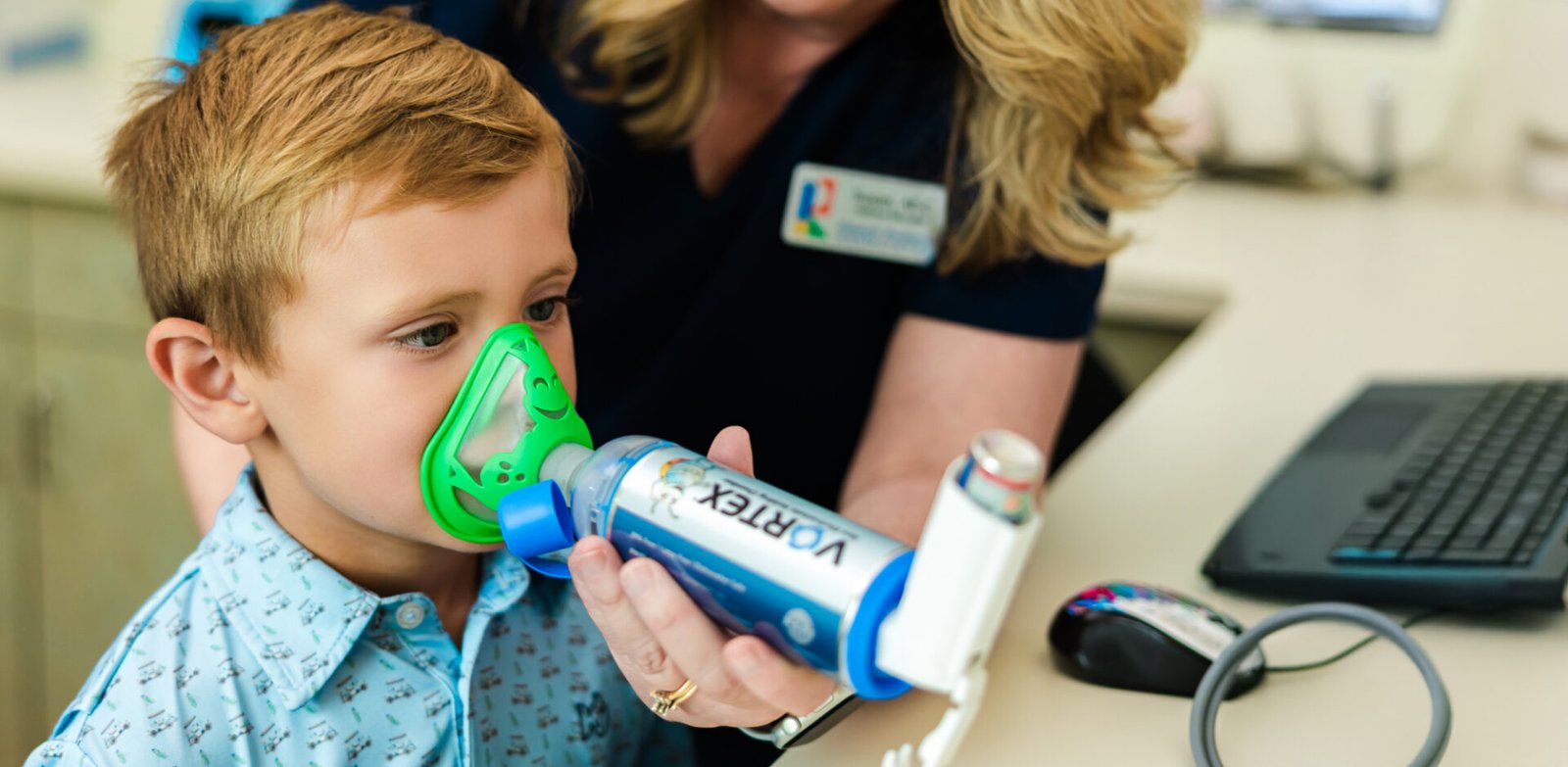
What Is a Spirometry Test?
Spirometry is one of the most common types of PFTs. During this test, a child breathes into a mouthpiece attached to a meter device. They will be asked to take a very deep breath and then exhale as forcefully and completely as possible. The spirometer records the amount of air exhaled and the speed of the exhalation.
A spirometry test offers several benefits in the evaluation of pediatric asthma, such as:
- Providing Objective Measurements of Airflow Limitation
- Helping Assess the Severity of Airway Obstruction
- Monitoring Changes in Lung Function Over Time
- Evaluating Responses to Medications
What Is a Volume Test?
A lung volume test measures the total amount of air the lungs can hold, and this includes the air that remains in the lungs after a full exhalation. The child sits inside a clear, airtight enclosure and breathes into a mouthpiece while measurements are taken. This test provides data on total lung capacity (TLC) and residual volume (RV), which adds data for a comprehensive respiratory evaluation. Another related test, the diffusion capacity (DLCO) test, measures how well gases transfer from the lungs to the bloodstream.
What Is a Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Test?
A fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) test is a noninvasive procedure that measures the level of nitric oxide in the air a child exhales. This gas is often present in higher amounts when there is a specific type of inflammation in the airways. Inflammation is heavily associated with asthma. For this test, a child breathes steadily into a tube connected to a portable device for about ten seconds, and the machine provides a reading almost immediately.
Learn More About Pulmonary Function Testing
Pulmonary function tests are valuable tools for understanding and managing lung health in children. These assessments provide detailed, objective data that complement a clinical evaluation and management plan. Some PFTs include spirometry, FeNO, and volume tests, but there are other options your doctor may offer. For more specific information regarding your child’s health, contact a pediatric specialist for personalized care.

Leave a Reply